Word clouds are used to visualize the most common words in a text. They are ideal for exploring large amounts of text and creating informative visualizations for presentations.

Generating a word cloud
Word Clouds can be generated for individual documents, document groups, document sets, or for all the documents in a project. Right-click on the level in the “Document Browser” for which you want to generate the word cloud and select the entry Word Cloud. You can also open the Word Cloud from the "List of Retrieved Segments", the Overview of Coded Segments and Overview of Paraphrases.
Alternatively, you can also open the Word Cloud function via the icon with the same name in the Visual Tools tab. A dialog box will then open in which you can select the relevant documents.
Stop word list: Excluding words in the Word Cloud
So that your Word Cloud does not consist mainly of insignificant words or words bearing very little meaning, you can create a stop word list of these words. The easiest way to do this is to open the Word Frequencies function in the Start tab of the Word Cloud window. The table that appears lists all the words in the text in their order of frequency.
Double-clicking on the green icon icon in front of a specific word will put it in the stop word list, which means it won’t be considered for Word Clouds. You can also select several words in the list (using Ctrl+ or ⌘+the left mouse button or ⇧+the left mouse button for an area in the list) and then right-click and select Add to Stop Word List. An icon with the same name is also available in the toolbar.
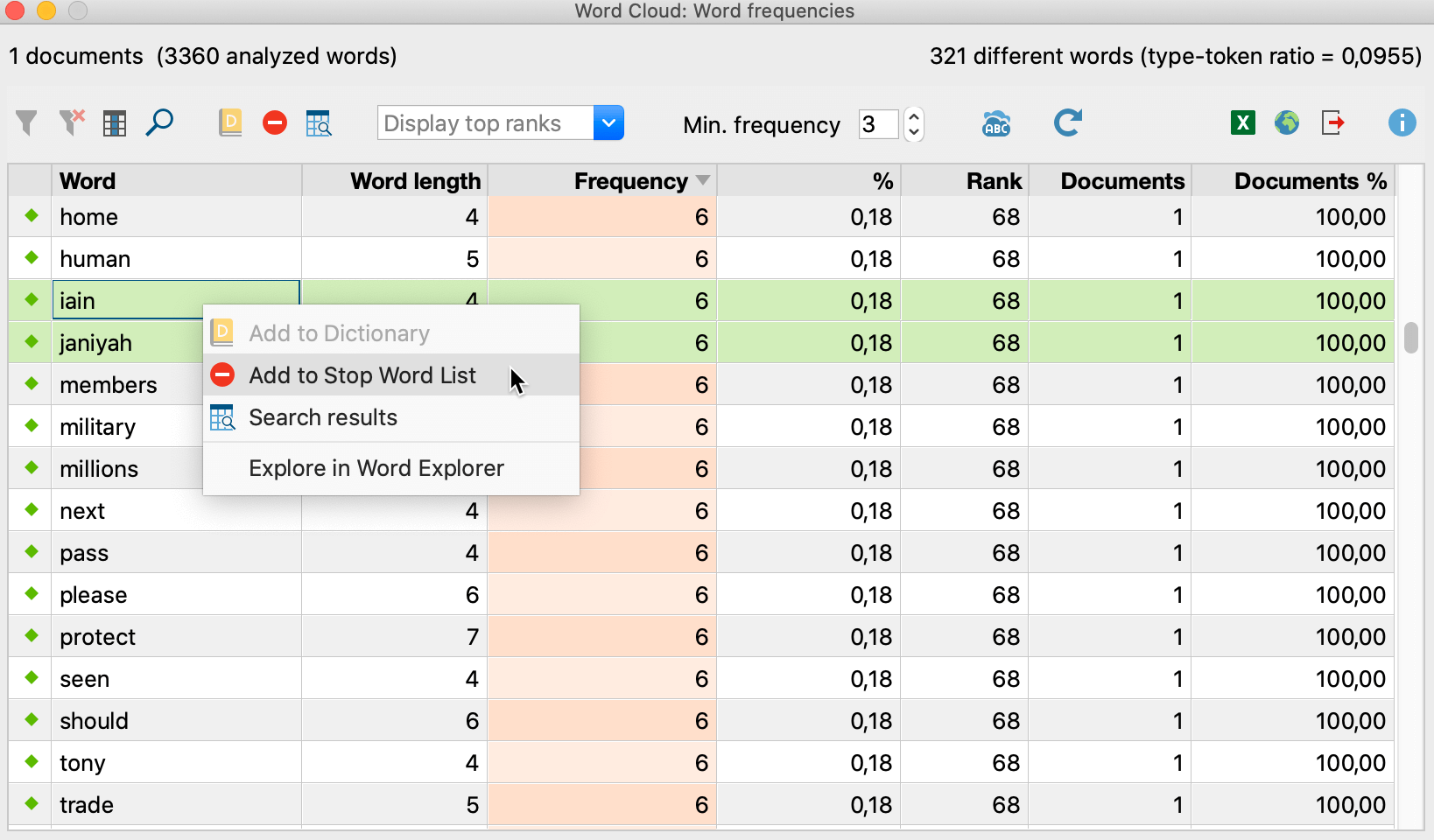
When you click the ![]() Refresh and apply stop word list, the Word Cloud is regenerated excluding words from the stop word list.
Refresh and apply stop word list, the Word Cloud is regenerated excluding words from the stop word list.
Editing the stop word list
The option Edit Stop Word List displays the complete stop word list used for word clouds in the current project. You can remove words from this list or add new words, although the way of doing this described above, by clicking in the frequency list, is actually much easier. Here you can also save and load already defined stop word lists to exchange them between projects.
Working with the word frequency list
Via Start > Word Frequencies you can open a list of all the words contained in the analyzed texts. This list shows, amongst other things, how often each individual word occurs. It is also possible to combine several words into one. To do this, click and drag one or more words onto another word with your mouse.
Adjusting the display
You can use the numerous options in the Start and Format tabs to customize the appearance of the word cloud, including the number of words displayed, their font, their shape, and color.
The Start tab
Word Frequencies – Opens a list of all words contained in the analyzed texts (without the stop words) and shows their frequencies. Words can easily be transferred from the word frequency list to the stop list.
Case Sensitivity – If this option is activated, a distinction is made between capitalized and non-capitalized words. For example, the words "earth", "Earth" and "EARTH" are treated as three different words.
Ignore Numbers – Excludes all "words" consisting only of numbers.
Lemmatize Words – When this option is activated, the inflected forms of a word are grouped together, for example, “go”, “went”, “gone” are all treated as “go” and “houses”, “housed”, “housing” are all treated as “house”.
Apply Stop Word List – Opens the list of all available stop word lists and the option to manage the stop word lists.
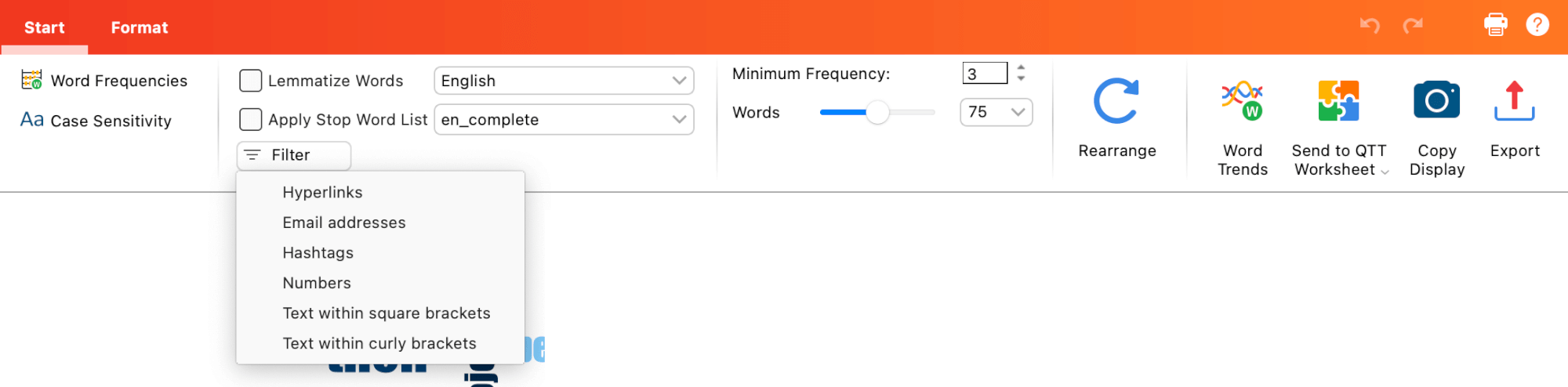
Filter – User can select text elements to be excluded from the Word Cloud, e.g. hyperlinks, email addresses.
Minimum Frequency – Defines the minimum number of times a word must occur in order to be displayed.
Words – Specifies how many words are visualized. You can use the slider to incrementally remove rarer words. If several words occur with the same frequency, words starting with letters earlier in the alphabet are selected first.
Rearrange – Regenerates the word cloud, placing words in different random locations.
The Format tab

Shape – Allows to define the outer borders of the Word Cloud. There are various variations to choose from:
- predefined forms (circle, ellipse, square, triangle)
- most frequent word
- a word you have entered
- a custom-selected image (is converted into a black and white image with the black area filled in, hence black and white images are best)
Alignment – Lets you define the alignment of words. The following options are available:
- Horizontal: All words are displayed horizontally
- Vertical: All words are displayed vertically
- Horizontal and vertical: Words are randomly aligned horizontally and vertically, the most common word is always displayed horizontally
- 30/45 degrees: Some words are additionally displayed at the selected angle diagonally upwards or downwards.
Colors – Lets you choose from a range of different color schemes.
Font / Bold – Lets you specify the font.
Word Distance – Defines the minimum distance between words
Smallest Word – Defines the size of the smallest word. The smaller this size is, the greater the difference in size compared to the most common words will be.
Size by – Defines the size of the words. Here you can choose from the following:
- Frequency: The more frequently a word occurs, the larger it is.
- Rank: The higher the rank of a word in the word frequency list, the larger the word. If you choose this option, the absolute difference between the word frequencies is irrelevant.
- Number of documents: The larger the word, the more documents it appears in. The number of documents can be seen in the list of word frequencies. This option only makes sense if you are analyzing several documents, as otherwise there will be no size difference between the words.
Scale – Influences the differences in size between common and rare words. The following options are available, which refer to the dimensions set under "Size by":
- Linear: The font size is linearly proportional to the word frequency.
- Most frequent greater: The font size is proportional to the square of the word frequencies. This makes the common words appear larger compared to the “Linear” option.
- Most frequent smaller: The font size is proportional to the root of the word frequencies. As a result, the common words appear smaller in relation to the "Linear" option.
Largest word – Lets you set the placement of the largest word: centered, somewhere near the edge, or at random.
Rearrange – Regenerates the word cloud, placing words in different random locations.
Display the occurrence of a word in the texts
The Word Cloud is interactively linked to the original texts:
- Clicking on a word will list all the occurrences of that word in the analyzed texts.
- If you hover your cursor over a word, the frequency of the word will be presented in a small information window (regardless of the selection made in “Size by:…”).
Autocode hits of a word
You can autocode all occurrences of a displayed word with a new code. This makes it possible, for example, to code all sentences in which an interesting word occurs in order to analyze these sentences further:
- Right-click on a word in the Word Cloud and select Autocode '‹word›' with a New Code.
- In the dialog that appears, you can enter the name for the new code or accept MAXQDA’s suggestion.
- In the subsequent dialog, you can specify the context that is to be coded: only the word or also the surrounding words, sentences, or paragraphs (paragraphs cannot be selected for PDF documents).

Save chart in "Questions – Themes – Theories"
In the Questions – Themes – Theories (QTT) you can collect and comment on all the important results of your project. Click the ![]() Send to QTT Worksheet icon in the Start menu ribbon to save the current view in a new or existing worksheet.
Send to QTT Worksheet icon in the Start menu ribbon to save the current view in a new or existing worksheet.
Exporting the Word Cloud
In the Start tab, there are two icons on the right that can be used to export the display:
![]() Copy Display – Copies the current view to the clipboard so that you can easily paste the display into reports or presentations by, for example, using Ctrl+V (Windows) or ⌘+V (macOS).
Copy Display – Copies the current view to the clipboard so that you can easily paste the display into reports or presentations by, for example, using Ctrl+V (Windows) or ⌘+V (macOS).
![]() Export – Exports the whole Word Cloud as a graphics file.
Export – Exports the whole Word Cloud as a graphics file.
