To systematize and group paraphrases, you can categorize them using codes. This function supports, among other things, the inductive and data-driven development of categories.
To start the categorization of paraphrases, proceed as follows:
- Activate the individual documents which include the paraphrases you would like to work with.
- Select Analysis > Paraphrase > Categorize Paraphrases (you have to click on the label "Paraphrase", not on the symbol above it).
The following interactive table window will then appear:
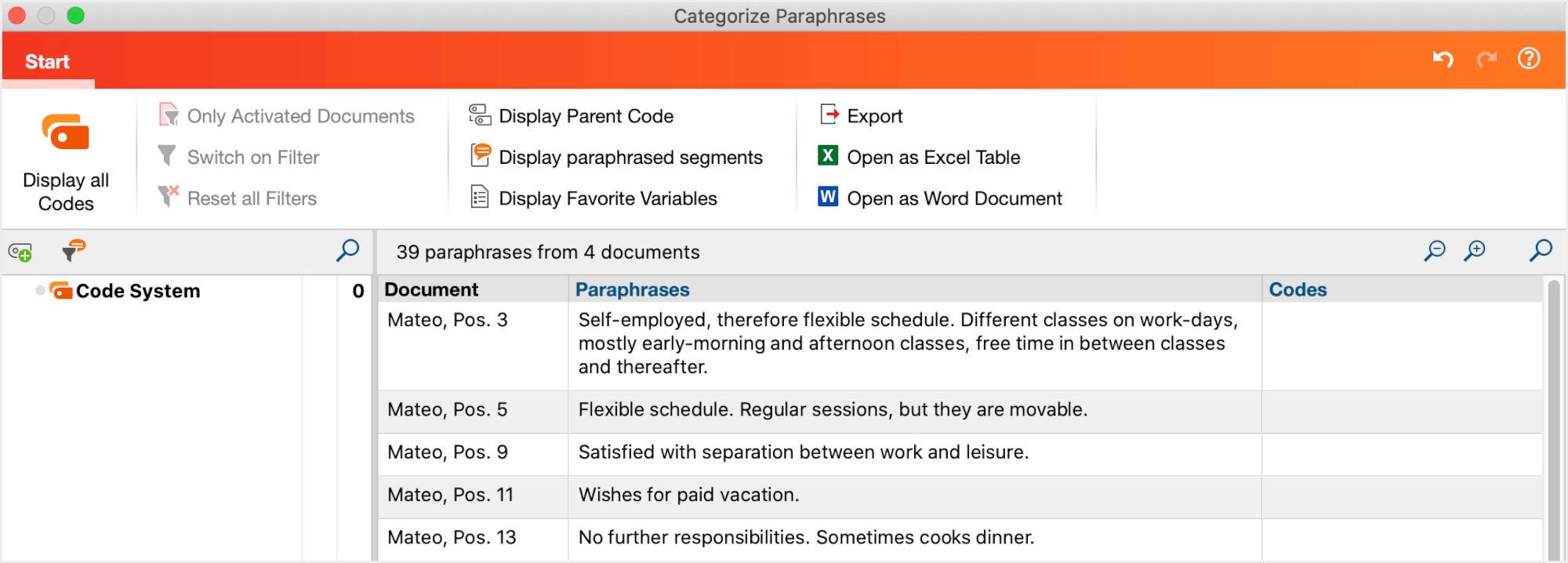
A code tree is displayed in the left field. When you open the function for the first time, it will still be empty. You can enter new categories here and then assigned them to individual paraphrases. The number at the end of the code line tells you how often the category occurs in your paraphrases. If you activate the function again later, all codes which have already been assigned to a paraphrase will be displayed in the code tree. So, you can easily pause your work on paraphrases and pick it up again later.
Above the code system there is a toolbar offering the following functions:
![]() Display only paraphrases from the selected category – if this option is enabled and you click on a category in the Code System, only the paraphrases of the selected category will be displayed.
Display only paraphrases from the selected category – if this option is enabled and you click on a category in the Code System, only the paraphrases of the selected category will be displayed.
![]() New code – creates a new category in the code system, which can be used to categorize your paraphrases.
New code – creates a new category in the code system, which can be used to categorize your paraphrases.
In the right field, all the paraphrases in your project will be displayed – each listed in a separate row. The number of currently listed paraphrases is displayed in the upper right corner of the window.
The individual columns contain the following information:
Document – Indication of origin, in which document and at which position the paraphrase was created
Paraphrases – Contains the paraphrase that has been written for the paraphrased text
Codes – The list of codes applied to the paraphrases
Paraphrased text – Contains the text that was paraphrased (this column is automatically hidden when the interactive table window is opened); <IMAGE> is displayed for paraphrased image segments, not the paraphrased image segment itself.
The table can be adjusted like all MAXQDA tables: The width and position of columns can be changed with the mouse, or by right-clicking on a column header. A click on the heading sorts the column in ascending order, another click in descending order.
The lines with the paraphrases can be sorted by drag and drop with the mouse so that similar paraphrases can be arranged one below the other, which is very helpful for categorization. Sorting remains as long as the project is open. When new paraphrases are added, they are appended at the bottom.
Functions in the Menu Ribbon “Start”
At the top of the “Categorizing Paraphrases” window there is a toolbar with the following functions:
![]() Display all codes – if this option is activated, not only the codes that have been newly created in the opened window or already assigned to a paraphrase as code are displayed in the "Code System", but all codes in this project.
Display all codes – if this option is activated, not only the codes that have been newly created in the opened window or already assigned to a paraphrase as code are displayed in the "Code System", but all codes in this project.
![]() Only activated documents – only the paraphrases of activated documents are displayed. The display of frequencies in the code tree is adjusted accordingly. If the documents were activated when this function was opened, this option is automatically activated.
Only activated documents – only the paraphrases of activated documents are displayed. The display of frequencies in the code tree is adjusted accordingly. If the documents were activated when this function was opened, this option is automatically activated.
![]() Filter – applies the filters you can define by right-clicking on the column heading and selecting Set Filter.
Filter – applies the filters you can define by right-clicking on the column heading and selecting Set Filter.
![]() Reset all Filters – removes filters from all columns.
Reset all Filters – removes filters from all columns.
![]() Display search toolbar – lets you to enter a search term to search for text in all or specific columns.
Display search toolbar – lets you to enter a search term to search for text in all or specific columns.
![]() Display Parent Code – in addition to the code, the "Codes" column also displays the parent code.
Display Parent Code – in addition to the code, the "Codes" column also displays the parent code.
![]() Display Paraphrased Segments – shows another column containing the paraphrased texts.
Display Paraphrased Segments – shows another column containing the paraphrased texts.
At the top right of the window there are also two icons for the local undo function:
![]() Undo – undoes the last action in the window.
Undo – undoes the last action in the window.
![]() Redo – redoes the last action in the window.
Redo – redoes the last action in the window.
Creating and Assigning New Categories
Paraphrases can be categorized using codes. You can always create a new code and assign it directly to a paraphrase:
- Right-click on the paraphrase and select Create and Assign New Code.
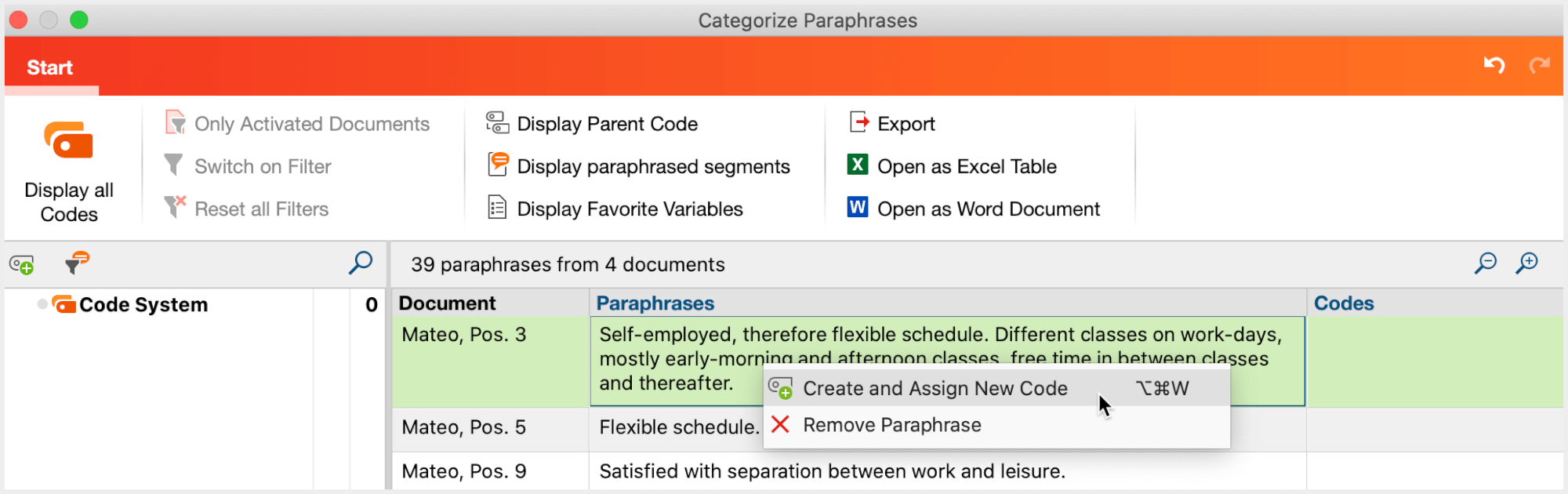
- In the dialog window that appears, you can enter a code name and assign a code color. You can also enter a description of the new code in the "Code memo" text box.
- After clicking OK the new code is added, displayed in the code tree on the left side, and assigned to the paraphrase.
This categorization is immediately made clear by the display of the code in the “Codes” column.

To assign a pre-existing category to a paraphrase, click and drag the row with the paraphrase to one of the displayed codes in the code tree.
You can also create categories without assigning them directly to a paraphrase: click on the green plus sign that appears when you hover with the mouse pointer over the word “Code System” or an existing code.
- To do this, click the New code icon in the toolbar,
- Use the key combination alt+N (Windows) or ⌘+⌥+N (macOS) or
- right-click on the top entry of the code tree and select New code.
Removing Assigned Categories
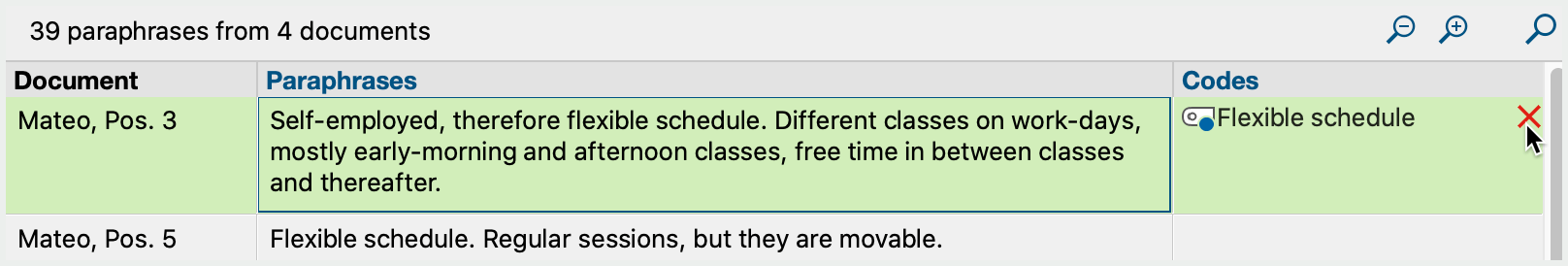
To remove a category assigned to a response, click the cross that appears when you move the mouse over a code in the "Codes" column.
Customizing Your Category System
Your category system can be customized throughout the entire analysis process. You can change the order of codes with the mouse and even insert them as sub-subcodes. By right-clicking on a code, all the functions from the overall "Code System" are available to customize your code system here:
- Delete code
- Sort subcodes (alphabetically or by category frequency)
- Change code color
- Create or edit code-memo
- Copy, move, paste coded segments
Exporting Paraphrases
Your current display can be exported via the usual icons at the top right of the window. All the rows (paraphrases) in the right field are always exported.
![]() Export – Creates a table as an Excel file (XLSX format), as a web page (HTML format) or as a text document (Word or RTF format).
Export – Creates a table as an Excel file (XLSX format), as a web page (HTML format) or as a text document (Word or RTF format).
![]() Open as Word document – Creates a Word document and opens it.
Open as Word document – Creates a Word document and opens it.
![]() Open as Excel spreadsheet – Creates an Excel document and opens it.
Open as Excel spreadsheet – Creates an Excel document and opens it.
