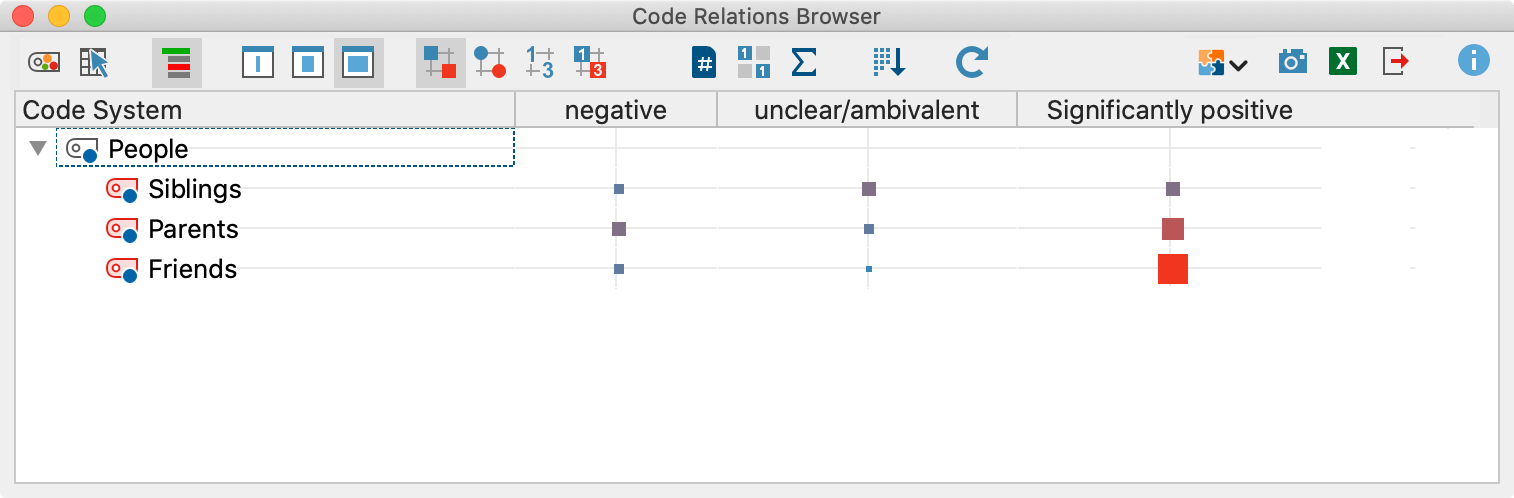
The Code Relations Browser (CRB) visualizes the relationships between codes and displays which codes co-occur how often within a document. From this graphical representation, it is much easier to see at a glance which codes are associated with each other than from a number matrix.
The CRB is constructed as follows: Codes form the columns and the rows. The symbols at the individual nodes indicate how many segments were coded with both the row's code and the column's code. The larger the symbol, the more segments there are.
You can open the CRB in different ways:
- Click on Code Relations Browser in the Visual tools menu tab,
- Use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+R (Windows) or ⌘+⌥+R (macOS)
- Click the Code Relations Browser icon
 in the "Retrieved Segments" window.
in the "Retrieved Segments" window.
Code Relations Browser options
After opening the Code Relations Browser an options window will appear, which allows you to change display options. Often, only the activated documents might be of interest, for example.
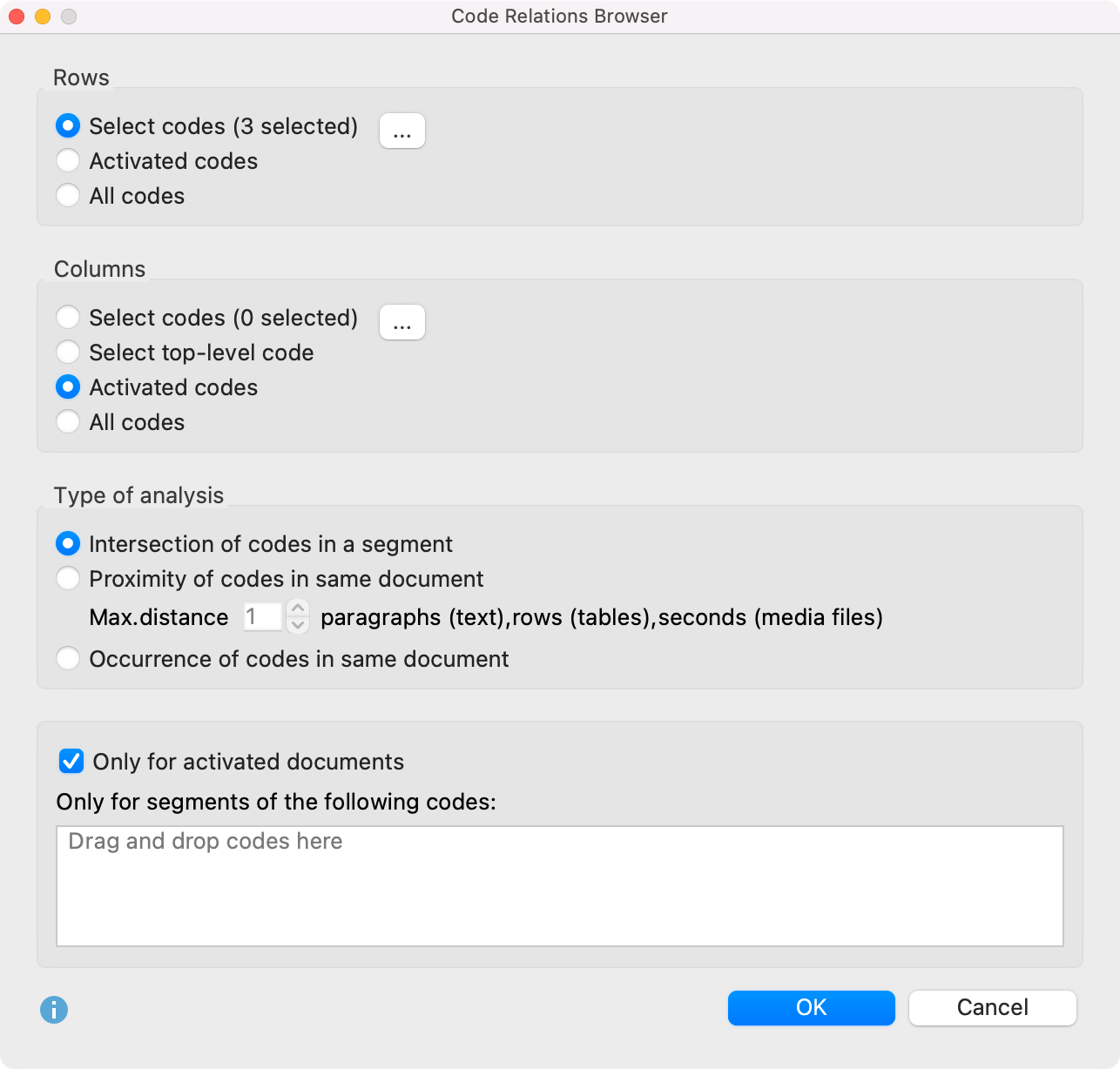
First, you have to decide which codes will be shown as rows:
Selected codes – Click the button with three dots to open a window where you can select codes to be displayed in the Code Relations Browser.
Activated codes – Only the activated codes will be shown as rows.
All codes – All codes will be shown, the order being the same as it is in the “Code System”.
A similar decision has to be made for the columns in the Code Relations Browser, with the additionally option of Choose top-level code. Selecting this option will open another dialog window after pressing OK, allowing you to select as many top-level codes as you want. The selected top-level codes and their subcodes will be shown as columns in the Code Relations Browser.
In the section “Type of analysis” you can select which relations MAXQDA will analyze:
Intersection of codes in a segment – Only “real” overlaps of codes will be analyzed, which means that a segment has to be coded with both codes and the codes need to overlap.
Proximity of codes in same document – Alternatively the Code Relations Browser can analyze how often two codes are present at a defined distance from one another. The distance can be set to a specific number of paragraphs (text), rows (tables), or seconds (audio/video).
If you search with the “Proximity” function and chose distance “0” you may find more hits than searching for intersections of codes. The function “Proximity” only evaluates if two codes are assigned somewhere in the same paragraph – not at the same segment.
Occurrence of codes in the same document – In this analysis type the Code Relations Browser shows in how many documents both codes occur. The codes do not have to intersect or be in specific proximity to each other.
In the lower area of the options window, you can restrict the Code Relations Browser display to certain documents or parts of documents coded with specific codes.
Only for activated documents - This setting is used to restrict the analysis to the documents currently activated in the “Document System”.
Only for segments of the following codes - This setting limits the search to segments coded with specific codes. If you drag a code from the "Code System" into the field with this mouse, MAXQDA only analyzes code co-occurrences within segments that have been coded with these codes.
Code Relations Browser toolbar
At the top of the screen, you will find the toolbar with the following functions:
![]() Code Map – Opens a "Code Map" visualization that displays the relations of the codes on a map. All codes that occur both in the rows and in the columns will be taken into account. The Code Map is created based on the code frequencies displayed in the Code Relations Browser. However, whether a code is collapsed in the left list or not will not be considered.
Code Map – Opens a "Code Map" visualization that displays the relations of the codes on a map. All codes that occur both in the rows and in the columns will be taken into account. The Code Map is created based on the code frequencies displayed in the Code Relations Browser. However, whether a code is collapsed in the left list or not will not be considered.
![]() Interactive Quote Matrix – Displays the coded segments in an interactive matrix. When choosing “Intersection of codes in a segment” as the type of analysis, only the overlapping part of the segments will be displayed in the output. In “Proximity of codes in same document” mode, segments that are close to each other will be outputted.
Interactive Quote Matrix – Displays the coded segments in an interactive matrix. When choosing “Intersection of codes in a segment” as the type of analysis, only the overlapping part of the segments will be displayed in the output. In “Proximity of codes in same document” mode, segments that are close to each other will be outputted.
![]() Display codes with hierarchy - If this option is activated, the codes are displayed in the hierarchical structure of the code system, even if the option "Only activated codes" is set, non-activated parent codes are also included to maintain the tree structure. If the option is deactivated, all codes are displayed on one level. If the "Only activated codes" option is activated, then only the activated codes are displayed.
Display codes with hierarchy - If this option is activated, the codes are displayed in the hierarchical structure of the code system, even if the option "Only activated codes" is set, non-activated parent codes are also included to maintain the tree structure. If the option is deactivated, all codes are displayed on one level. If the "Only activated codes" option is activated, then only the activated codes are displayed.
![]()
![]()
![]() Names, columns: none/short/full – There are three possible options for displaying the names of documents, document groups, document sets, and focus group participants in the column headings:
Names, columns: none/short/full – There are three possible options for displaying the names of documents, document groups, document sets, and focus group participants in the column headings:
- no names: The column headers remain empty.
- short names: Display of the first eight characters (usually recommended).
- full names: Full name will be displayed.
![]() Display nodes as squares.
Display nodes as squares.
![]() Display nodes as circles.
Display nodes as circles.
![]() Display nodes as values.
Display nodes as values.
![]() Display heatmap with values.
Display heatmap with values.
![]() Count hits per document only once – The Code Relations Browser display will be based not on the number of code relations but of documents, meaning it will analyze only whether a code relation occurs in a document and not how often. For collapsed subcodes, the code relation frequencies of the subcodes will be summed up. When using the analysis mode “Occurrence of codes in same document” this option is selected automatically and hidden from the display window.
Count hits per document only once – The Code Relations Browser display will be based not on the number of code relations but of documents, meaning it will analyze only whether a code relation occurs in a document and not how often. For collapsed subcodes, the code relation frequencies of the subcodes will be summed up. When using the analysis mode “Occurrence of codes in same document” this option is selected automatically and hidden from the display window.
![]() Binarize view – If selected, the Code Relations Browser will show only whether a code relation is present or not; all symbols are displayed in the same size. For collapsed subcodes, the code relations frequency of the subcodes will not be aggregated.
Binarize view – If selected, the Code Relations Browser will show only whether a code relation is present or not; all symbols are displayed in the same size. For collapsed subcodes, the code relations frequency of the subcodes will not be aggregated.
![]() Sum – displays the sum of rows and columns.
Sum – displays the sum of rows and columns.
![]() Sort columns by similarity of code pattern – By default, the order of columns is based on the “Document System”. Clicking this icon, sorts the current display, so that columns with many codes are placed on the left and columns with few codes on the right. Columns with identical code patterns and frequencies are placed next to each other. This feature is helpful to identify patterns and regularities and to find similarities between cases or groups.
Sort columns by similarity of code pattern – By default, the order of columns is based on the “Document System”. Clicking this icon, sorts the current display, so that columns with many codes are placed on the left and columns with few codes on the right. Columns with identical code patterns and frequencies are placed next to each other. This feature is helpful to identify patterns and regularities and to find similarities between cases or groups.
![]() Refresh – updates display via the Refresh function.
Refresh – updates display via the Refresh function.
Information window for a node
Each symbol in the matrix represents the number of co-occurrences of the two codes. The larger the symbol, the larger the number of co-occurrences. If you hover over a node with your mouse, a small window appears informing you about the node codes and the number of their relations.
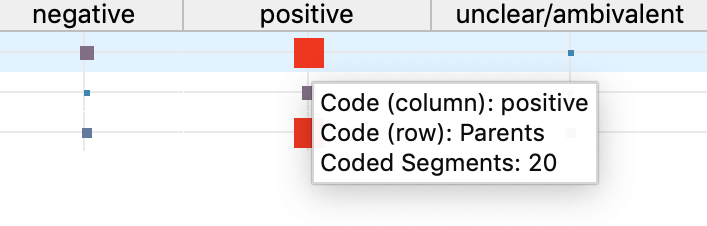
How are symbol sizes determined?
How MAXQDA determines the symbol sizes is explained in detail in the Code Matrix Browser section.
Compiling the coded segments for a node
You can jump to the segments with co-occurring codes by double-clicking on the node representing them. MAXQDA will compile all the segments in question in the “Retrieved Segments” window. The CRB can remain open, so you can quickly go from one set of co-occurring codes to another.
If you are in mode “Occurrence of codes in same document” and double-click on a node, all of the documents in which the relation occurs are activated.
Export adjacency matrix for network analysis software packages
If you want to perform a network analysis of categories with a program like Gephi, you can export the results of the Code Relations Browser as an adjacency matrix:
- Clicl the Export icon
 at the top right of the window.
at the top right of the window. - In the file dialog, select "Adjacency Matrix (*.xlsx)" as the file format.

MAXQDA exports the frequencies of relations as follows:
- The matrix is exported as if all codes were expanded.
- Codes, that are displayed only in the columns are added to the rows and vice versa. This creates a symmetrical matrix.
- If the name of a code occurs more than once, the name of the parent code is prefixed to ensure uniqueness of the code names.
Store view in Questions – Themes – Theories
In the Questions – Themes – Theories window, you can collect and comment on all the important results of your project. Click the ![]() Send to QTT Worksheet icon in the upper right corner to save the current view in a new or existing worksheet.
Send to QTT Worksheet icon in the upper right corner to save the current view in a new or existing worksheet.
Exporting the Code Relations Browser
In the CRB toolbar, there are three icons on the right that can be used to export the display:
![]() Copy current display as an image to clipboard - Copies the visible area to the clipboard so that you can easily paste the results into reports or presentations by, for example, using Ctrl + V (Windows) or ⌘+V (macOS).
Copy current display as an image to clipboard - Copies the visible area to the clipboard so that you can easily paste the results into reports or presentations by, for example, using Ctrl + V (Windows) or ⌘+V (macOS).
![]() Open as Excel table – Exports the complete matrix with the frequencies as an Excel file and opens it. The columns and rows are swapped to allow easy import into SPSS and other statistical software.
Open as Excel table – Exports the complete matrix with the frequencies as an Excel file and opens it. The columns and rows are swapped to allow easy import into SPSS and other statistical software.
![]() Export – Exports the complete matrix with the frequencies in Excel or HTML format. The columns and rows are swapped to allow easy import into SPSS and other statistical software. Exporting as a graphics file is also possible.
Export – Exports the complete matrix with the frequencies in Excel or HTML format. The columns and rows are swapped to allow easy import into SPSS and other statistical software. Exporting as a graphics file is also possible.
