The MAXQDA Stats Variable List allows you to manage all the variables of a data set. This is the place to define the variable names and value labels, and also to set missing values for a variable. New variables can also be created in the Variable List.
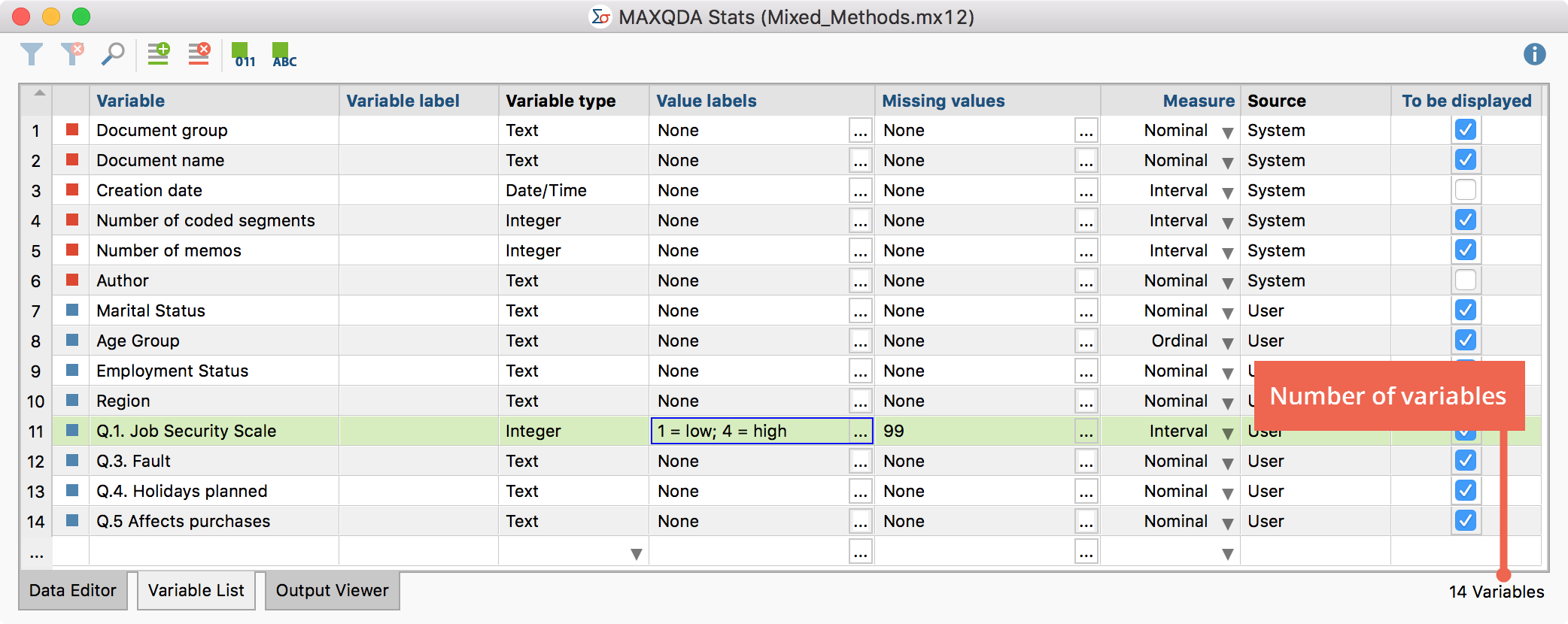
In the first column there is a consecutive numbering of the variables. The variables in the Data Editor are displayed from left to right, corresponding to this numbering. The number of variables in the current data set are displayed on the bottom right in the status bar.
The other columns include the following features:
Variable – This column is a mandatory column, meaning each variable requires a variable name. To create, for example, a frequency table or a crosstab, you can select the name of individual variables.
Variable label – In addition to the variable name, it is possible to assign a label to a variable. In MAXQDA this label can be up to 255 characters in length and include any character. The variable label will appear in selection dialogs and results tables in the place of the variable name for easier interpretation.
Variable type –The same types of variables can be used in MAXQDA and MAXQDA Stats: text, integer, floating point, date/time, and Boolean (true/false).
Value labels – In statistical data sets, answers are often coded with numbers, for example 1 for “low” and 4 for “high”. Assignment of texts to the encoded numbers is done via value label and will appear in this column. At the top of the figure it is shown that for the marked variable “Q.1. Job Security Scale” the text labels “low” and “high” were assigned for the scale endpoints 1 and 4.
Missing values – In this column, the values are displayed which are to be counted as missing for the respective variable and therefore not to be included in the analysis.
Measure – Here you can set the measurement level of a variable. You can choose between three levels: “Interval”, “Ordinal” and “Nominal”.
Source – This column provides information about the origin of a variable. Variables automatically generated in MAXQDA carry the identifier “System”, user-defined variables carry the identifier “User”. Variables with the origin “Code” are codes to which the function “Transform into document variable” was applied in a MAXQDA project. Variables carrying the identifier “Dictio” are the result of a dictionary-based enumeration of category frequencies using MAXDictio.
To be displayed – From this column, you can control the display of variables in the Data Editor. To hide a column, remove the check mark by clicking a cell.
